Tendonitis and Tenosynovitis

At FORM Hand Therapy, our hand therapists have extensive education and training in the rehabilitation of tendon repetitive injuries and tendon overuse conditions resulting in tendonitis or tenosynovitis. (Tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon often developing after degeneration (tendinopathy). Tenosynovitis is tendinitis with inflammation of the tendon sheath lining.)
The following are just a few tendon overuse and repetitive use conditions we treat. These conditions may be treated nonsurgically with splints, exercises, and modification of activities, but sometimes require surgery and post-surgical therapy.
- Biceps Tendonitis
- De Quervain’s Tendonitis
- Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
- Trigger Finger
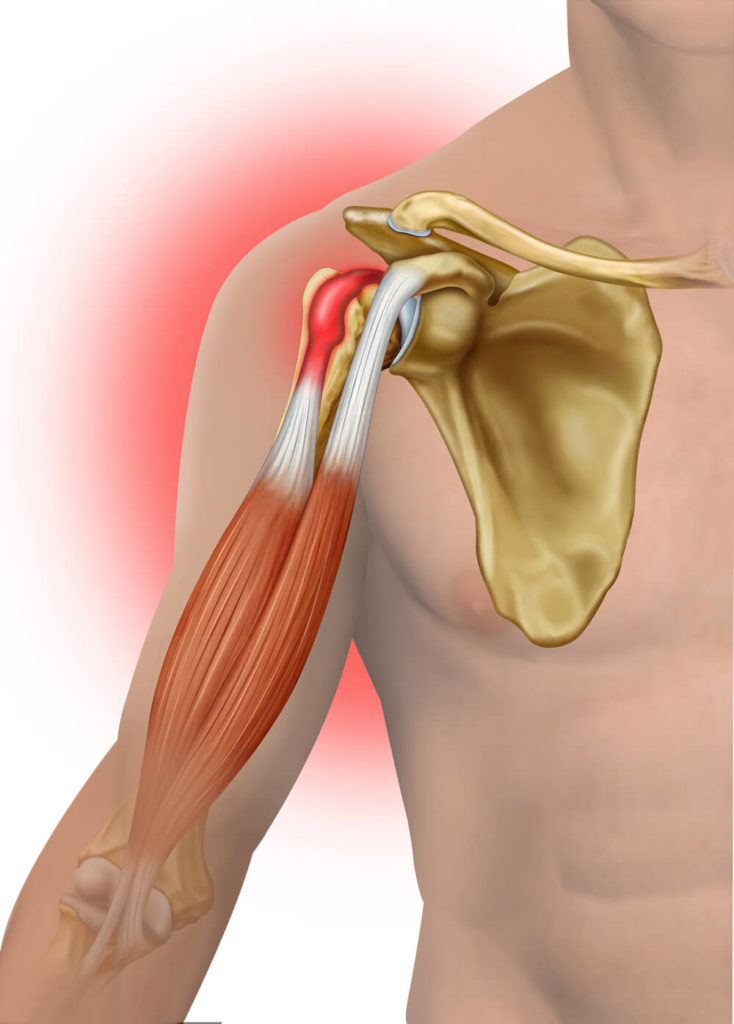
Biceps Tendonitis
The biceps muscle is located at the front of your upper arm with its main tendon attached to the front of the shoulder. Biceps tendonitis occurs when this tendon becomes inflamed from irritation that can be due to normal wear and tear, prolonged repetitive movements, or related to other shoulder conditions such as arthritis, shoulder impingement, chronic dislocation/instability, and cartilage tears. If inflammation of the tendon continues, it can cause the tendon covering (tendon sheath) to become thicker or cause the tendon to tear.
Symptoms
- Pain in the front of the shoulder.
- Shoulder tenderness to touch.
- Worsening pain and/or muscle weakness with overhead or lifting movements.
- Clicking sound or sensation with shoulder movement.
- Radiating pain to the elbow or towards the neck.
Treatment
Biceps tendonitis is usually treated with physical therapy and rarely needs surgical intervention unless there are other shoulder conditions present that require surgery. Once your doctor has determined that your shoulder pain is due to biceps tendonitis and recommends physical therapy as part of your treatment plan, our therapists will design a comprehensive therapy program for you. They will work with you to tailor a program specifically based on the severity of your tendonitis, other shoulder conditions present, and your goals for recovery.
We understand that there are specific activities that are important to you and essential to your day-to-day duties. Our well-rounded, hands-on approach ensures that you stay motivated and disciplined with your therapy program to get you back to pain-free function. Your therapy program will include strengthening and range-of-motion exercises for balance and support of shoulder muscles, hands-on manual therapy for assisted movement and flexibility, and specific activity training and proper body mechanics to reduce the strain on your shoulder.
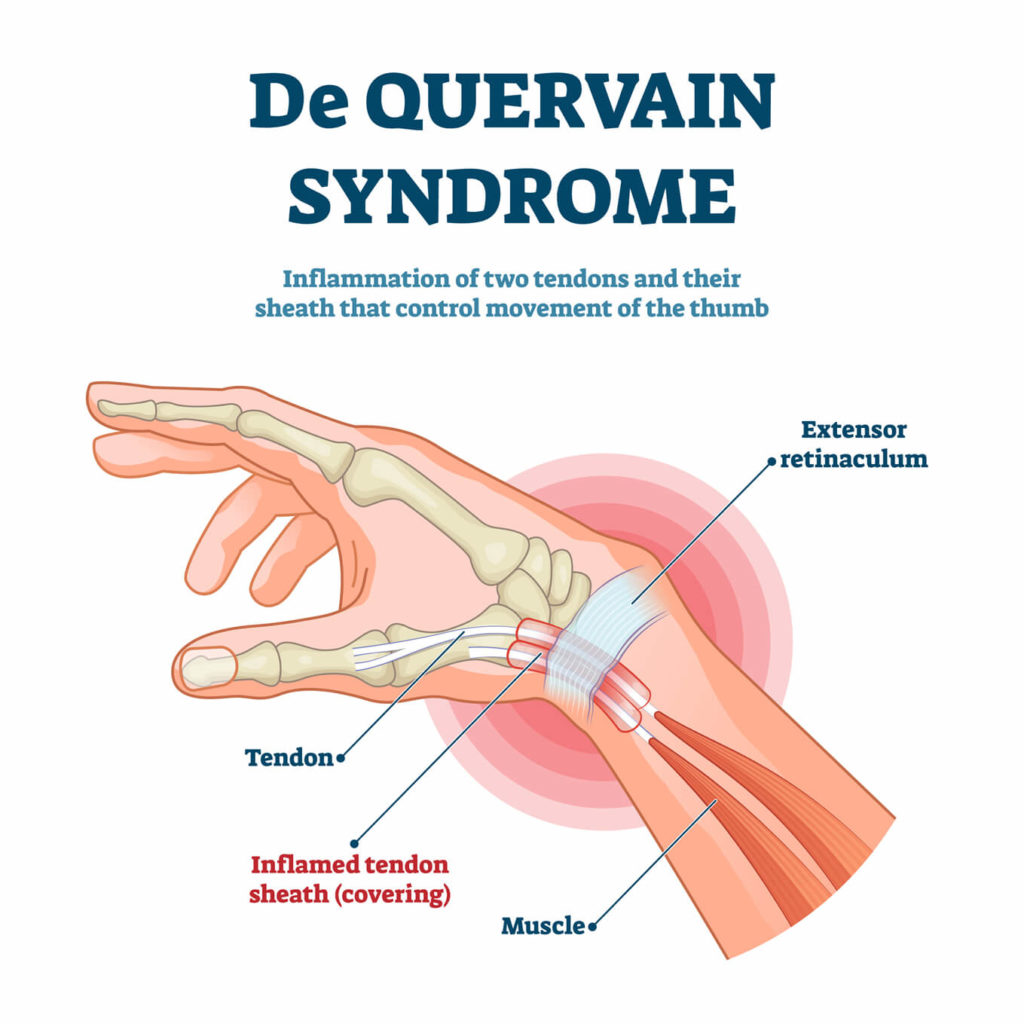
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist that are involved in the extension of the thumb joint. These tendons are usually strained from repetitive motion injury.
Symptoms
- Pain at the base of your thumb.
- Difficulty moving your thumb or wrist that involves grasping or pinching.
Nonsurgical Treatment
If you are referred to FORM Hand Therapy for conservative treatment of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, our hand therapists will make modifications to activities that aggravate your symptoms. They will provide an exercise program for stretching and strengthening. They may also create a custom fabricated splint to stabilize the wrist and thumb to assist in resting the tendons in the affected compartment.
Post-Surgical Treatment
If surgery is needed for more severe symptoms, our hand therapists will make every effort to assist in your return to full hand function through a gradual progression of strengthening exercises. These exercises include gentle active range of motion and tendon gliding exercises and then progresses to grip and pinch exercises.
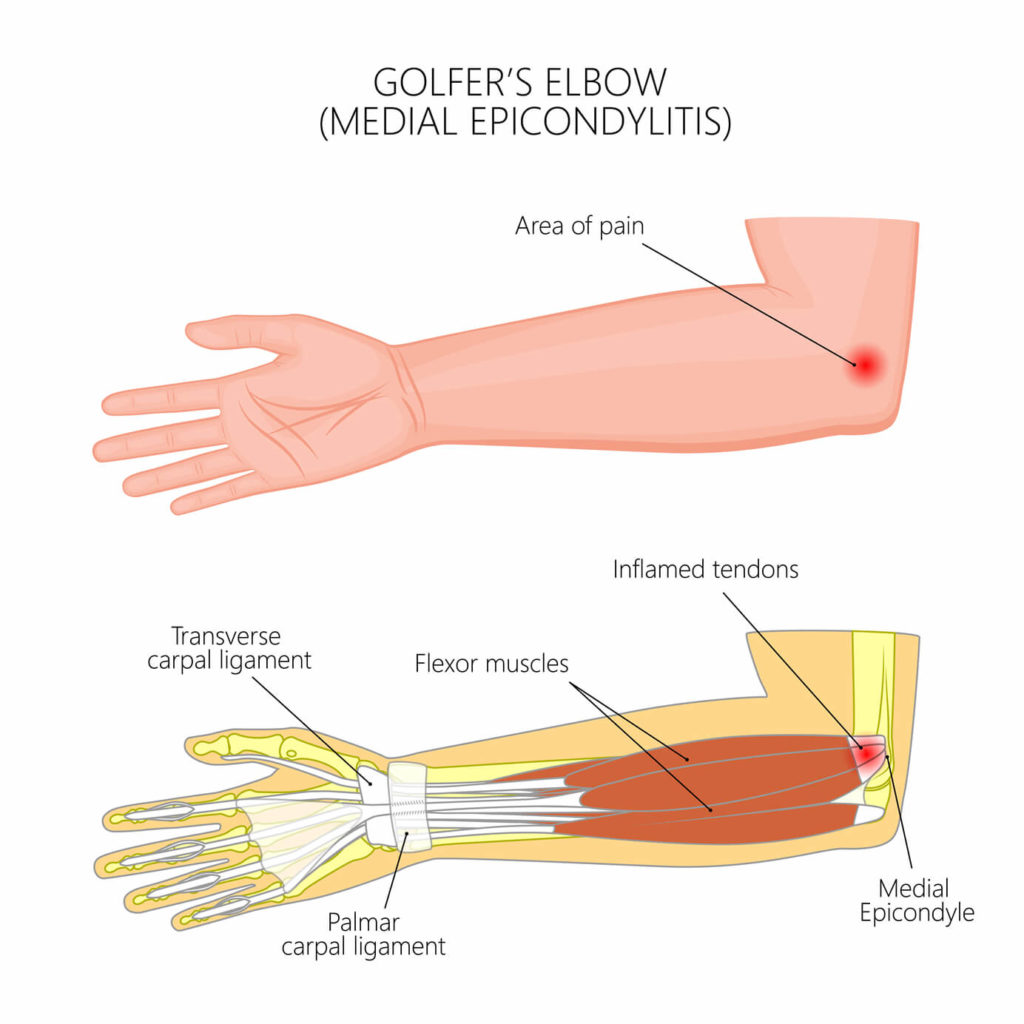
Golfer’s Elbow
Medial epicondylitis or golfer’s elbow is tendonitis of the inside of the elbow joint. The repetitive overuse of these muscles causes inflammation of the tendons, the connective tissue between the muscle and the bone. While golf is a common cause of medial epicondylitis, it can also be caused by any repetitive motion or sharp sudden movement that involves the elbow.
Symptoms
- Pain at the inside of the elbow
- Elbow stiffness
- Numbness or tingling in fingers
- Hand and/or wrist weakness
Treatment
Treatment of golfer’s elbow can include physical therapy, anti-inflammatories, splinting, and stretching. In some cases, cortisone injections may be suggested when other treatments are not effective.
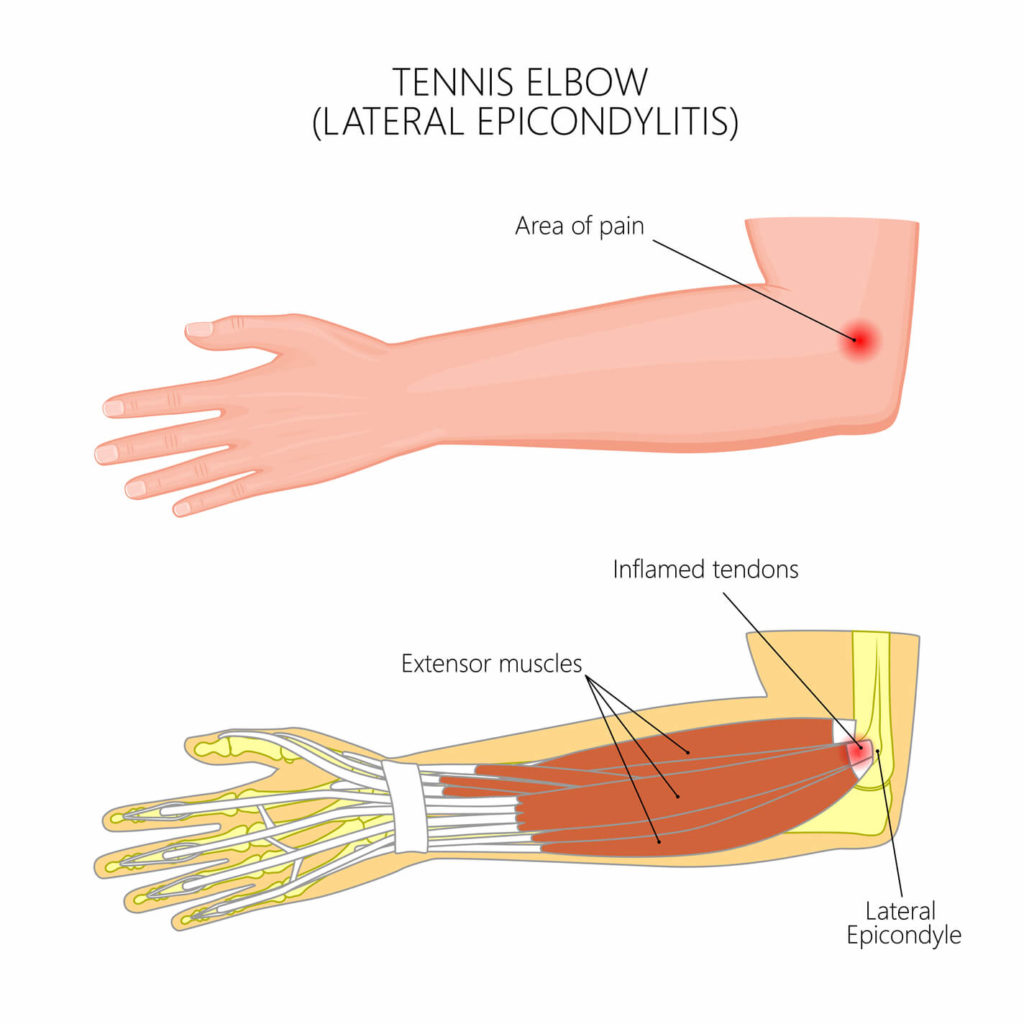
Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis is a tendonitis of the outside of the elbow, unlike golfer’s elbow which affects the inside of the elbow. Tennis elbow is mainly caused by repetitive use during tennis or any other activity that uses the hand or wrist muscles. These muscles share a common tendon that is connected to the portion of the elbow bone known as the lateral epicondyle. As tiny tears happen over time and with age, the body has a more difficult time repairing itself which leads to symptoms of tennis elbow.
Symptoms
- Pain while bending the wrist
- Tenderness or pain in the elbow
- Difficulty picking up heavy objects
- Weakness in the hand and wrist
Treatment
Treatment for tennis elbow includes physical therapy, stretching, rest, and/or anti-inflammatory medication. If the symptoms of tennis elbow persist with the above treatment, then cortisone injections and minimally invasive surgery are other options for tennis elbow.
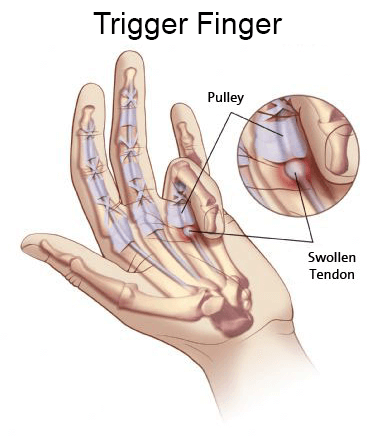
Trigger Finger
Trigger finger is a common condition that affects the tendons that flex the fingers and the thumb. The flexor tendons of your fingers and thumb travel down tunnels guiding them down the digits into the palm. If the tendon becomes inflamed, narrowing the space in the tunnel as it tries to glide, the tendon will get trapped, and cause the digit to get stuck in a flexed or occasionally extended position. Symptoms can occur with overactivity of repetitive gripping.
Symptoms
- Stiffness in the finger, especially in the morning.
- A popping or catching sensation.
- Pain with bending the finger.
- Inability to straighten the finger.
- A nodule/lump that is tender in the palm at the base of the affected finger.
Treatment
Your doctor may refer you to a hand therapist for nonsurgical and post-surgical treatment of trigger finger depending on the severity of the condition. For nonsurgical treatment, our hand therapists can fabricate a custom splint to restrict finger movement, teach you exercises to avoid finger stiffness, and modify activities while the finger is healing. The goal of hand therapy following trigger finger surgery is to improve range of motion and regain function of the hand.
Contact Us
If you have a question about whether your condition should be treated by one of our hand therapists, call FORM Hand Therapy at (510) 350-3030. If you are not currently under the care of a physician for your condition or would like to be evaluated by an Orthopedic Surgeon specializing in hand, wrist and elbow conditions, schedule an appointment online.
